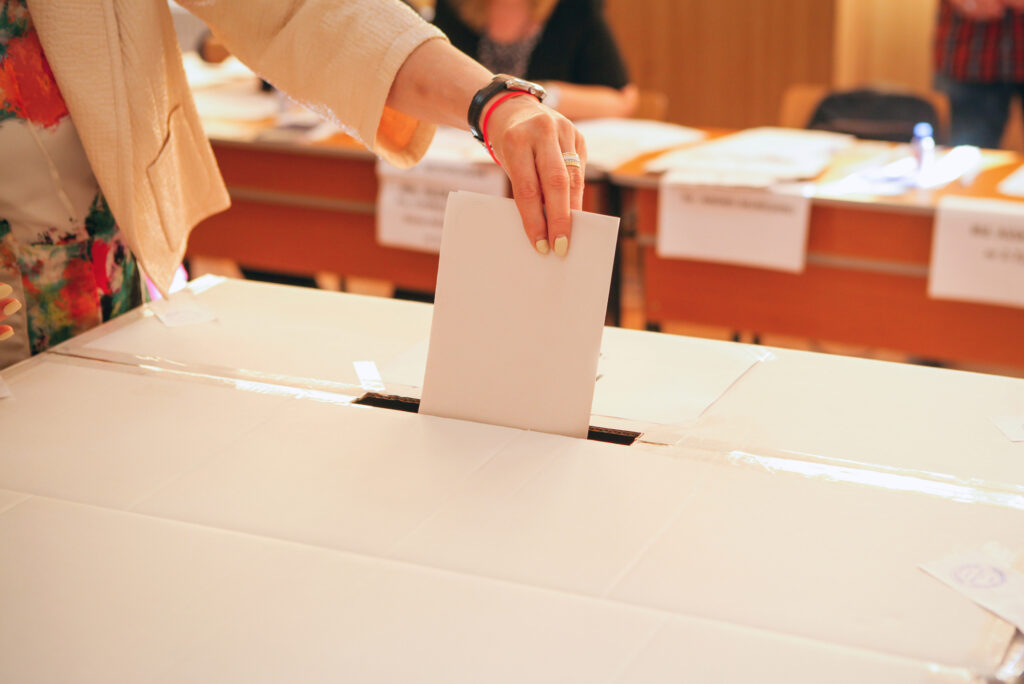
Homeowners Associations (HOAs) play a vital role in maintaining the safety and appearance of neighborhoods across the United States.
With over 370,000 HOAs representing 53% of owner-occupied households, each community has a unique way of functioning. One crucial aspect is the HOA board, which is composed of volunteer members elected through community-run HOA elections.
This guide explores common HOA election pitfalls and how to organize successful elections and ensure accurate results.
1. Engage the Community
Engaging the community early helps ensure a high voter turnout.
Encourage participation through events, flyers, social media posts, or a dedicated website. Establish a timeline covering key phases, including notification, proxy distribution, information dissemination, voting, vote counting, and prompt communication of results.
By conveying information quickly and setting a timeline for events, all members can feel secure knowing the electoral process is managed effectively and honestly. Failure to adhere to this timeline or required processes may result in having to redo the election or involving a third party.
Also read: Minimize Risk with 6 Best Practices for HOA Email Communications
2. Understand HOA Bylaws
One of the most critical aspects of HOA elections is understanding the roles that govern them.
Study the HOA bylaws to clarify voting requirements, term lengths, and other rules related to candidate and voting qualifications, proxy usage, voting methods, voting periods, and nomination procedures. Bylaws provide guidelines for various scenarios, such as filling vacancies in case of resignations. HOAs must enforce these collectively agreed-upon rules to minimize confusion and establish authority.
3. Comply With State and Local Laws
In addition to community bylaws, HOAs must adhere to state and local regulations that impact HOA operations and board member elections. These state and local laws vary in many ways, such as California’s requirement for HOAs to file Articles of Incorporation to classify them as non-profit corporations.
For HOA elections, these laws may determine term limits, third-party participation requirements (such as an inspector during voting), and other ways HOAs must adhere to corporate governance laws.
Understanding these laws minimizes election risks and ensures legal compliance.
4. Fill all Available Positions Appropriately
While many roles may exist within an HOA, elections typically revolve around four commonly essential positions.
- The President heads the board, representing the community internally and externally, overseeing meetings, and managing community affairs.
- The Vice President assists the President and acts as a replacement when needed.
- The Secretary maintains meeting records and manages correspondence to ensure compliance with HOA bylaws and laws.
- The Treasurer handles financial matters, managing budgets, payments, deposits, and dues collection.
5. Verify Candidate and Voter Eligibility
Members must fulfill requirements denoted by HOA bylaws or state regulations to be eligible. The most common requirement is that candidates and voters must be homeowners with specific qualifications, meaning renters are excluded from the process.
Some HOAs will have qualification requirements, such as:
- Residing in the community for a set number of years
- Being involved in the community, for example, as part of a committee
- Attending a required number of HOA meetings in the past
6. Account for All Types of Voting
Standard voting methods include:
- Written or electronic ballots
- By proxy, where another member is authorized to vote on someone else’s behalf
- Secret ballots that omit personal information
Renters typically cannot vote or serve as proxies, though exceptions exist.
7. Follow Proper HOA Election Processes
Processes will vary from HOA to HOA, but typically, elections should follow a common pattern.
- Notification: Send notices to all members about upcoming elections that specify positions, outline nomination deadlines, and clarify procedures.
- Nomination: Community members nominate candidates, adhering to applicable rules and regulations.
- Pre-ballot notices: Distribute pre-ballot notices that detail candidates, voting instructions, and counting locations.
- Voting: Accept votes until the voting period ends—either electronically or in-person.
- Results: After voting, count and announce the results promptly.
Also read: Effective Record Keeping and Procedures for HOA Meetings
8. Adhere to Quorum Requirements
Many HOAs will require a minimum number of participants—a quorum—to conduct the election.
In the case of HOA elections, quorum rules determine attendance or votes needed for a valid election, highlighting the importance of proxy voting and ample election notice. If HOA bylaws state that a quorum is required and not enough members vote, the voting period must be extended or redone entirely.
9. Count Votes Accurately
Ensuring votes are secure and legitimate is crucial to the election process.
Ballots must be stored where only authorized members can access them to prevent tampering. Additionally, the board should account for varying security concerns for digital and physical ballots before the voting period begins. Count votes transparently in the presence of an inspector if required (some states may mandate a third-party inspector is present). Communicate results to absent members promptly and document the entire process for transparency and future reference.
10. Protect Yourself from Potential Liabilities
By following these steps and staying informed about HOA bylaws and relevant laws, communities can ensure successful and transparent HOA elections, fostering trust and effective governance.
McGowan Program Administrators offers Community Association Insurance with extensive coverage options to ensure your HOA or community association gets the protection it needs. With decades of experience in providing comprehensive insurance plans, McGowan MPA has the expertise you need to navigate potential liabilities safely.